Purine-based scaffold using a peptide cleavable linker to induce an anti-tumor immune response.
How It Works
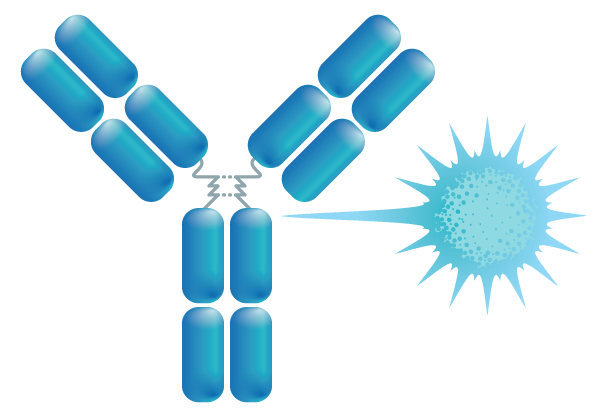
This modality consists of a tumor specific antibody conjugated to a toll-like receptor 7 agonist (TLR7a) immunostimulatory small molecule via a peptide cleavable linker designed to induce an anti-tumor immune response. Upon binding of the antibody to its target on the tumor cell, the Fc region of the antibody engages a phagocytic immune cell (monocytes, dendritic cells, macrophages, and neutrophils) leading to payload release, TLR7-agonism, induction of cytokine expression, and an anti-tumor response.
How We Differ
Systemic toxicities and lack of efficacy have hampered recent immune-stimulating antibody conjugates (ISACs) clinical development but provide incentive to identify novel payloads. We have developed purine-based immunostimulatory drug conjugates that have demonstrated strong activity on both murine and human immune cells in vitro. This cross-species activity negates the use of surrogate molecules for in vivo studies, providing greater translational relevance than other platforms.